

For example, I might be able to measure a distance to within 1% precision given a confidence level of 99%. One can never know for sure if two unequal measurement results are just caused by dumb luck or if they are “really” different, but one can say with some quantified confidence level that the difference wasn't a fluke. It's a parameter that includes repeatability and random noise that prevents us from being able to decide if two different measurement results are different because they are measuring two different true values of the measurand, or because random errors have produced the difference. In that sense, ordinate resolution is a specification of the precision in the ordinate. When speaking just about an ordinate in isolation, resolution can be defined as the statistical blurring caused by measurement uncertainty. The minimum interval possible between two unequal ordinate measurements by a measurement system when measuring a DUT. Nadovich, in Synthetic Instruments, 2005 Ordinate Quantization Interval
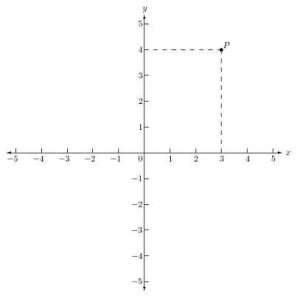
In quadrant 1, both x and y coordinates are positive. In quadrant 4, the x-coordinates are positive and the y-coordinates are negative. All the quadrants are different from each other based on the position and symbol of the x and y-coordinates. These are formed by the intersection of the x and y axes and are named Quadrants I, II, III, and IV. The x and the y-axes divide the plane into four graph quadrants. For example, if someone says a point is located in quadrant II, immediately is understood that the x coordinate of the point is negative and its y-coordinate is positive. The quadrants are used to explain the position of a point on the coordinate plane. Other than this, quadrant II has negative x-coordinates and positive y-coordinates, quadrant III has both negative coordinates and quadrant IV contains the positive values of x but negative values of y. Quadrant I contains the positive values of x and y, so it is considered to be a positive quadrant. Quadrant IV is on the lower right-hand corner of the plane.Quadrant III is on the lower left-hand corner of the plane.Quadrant II is on the upper left-hand corner of the plane.Quadrant I is on the upper right-hand corner of the plane.The 4 quadrants are numbered in the following way: We get 4 quadrants when the axes intersect each other. In the above example, ordinate = 6 means, starting from the origin, we need to go along the y-axis in a positive direction (up) up to 6 units.įAQs on Quadrant What is the Definition of Quadrant in Math?Ī quadrant can be defined as a part of a cartesian plane that is obtained when the two axes intersect each other. The ordinate gives information about the vertical distance of the point from the origin and its sign tells the direction, i.e., above or below the origin.For example, abscissa = -4 means, starting from the origin, we need to go along the x-axis in a negative direction (left) up to 4 units. The abscissa gives information about the horizontal distance of the point from the Y-axis and its sign tells the direction, i.e., left or right.Without even plotting it on a graph, by observing its sign (-ve, +ve) we can make out that it lies in quadrant II. For example, we are given a point P (-4,6). This gives an idea about the quadrant in which the given point lies.
#DEFINE ABSCISSA HOW TO#
To understand how to plot a point in the four quadrants, we need to observe the signs of an x-coordinate (also called abscissa) and a y-coordinate (also called ordinate). The numbers in the quadrant are expressed in the ordered pair (a, b) where 'a' is the x- coordinate and 'b' is the y-coordinate.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
